IntroductionIn many computing environments, data storage space is a limited resource. Therefore, it might be more important for you to conserve data storage space than to conserve other resources. When you store your data in a SAS data file, you use the sum of the data storage space that is required for the following:
|
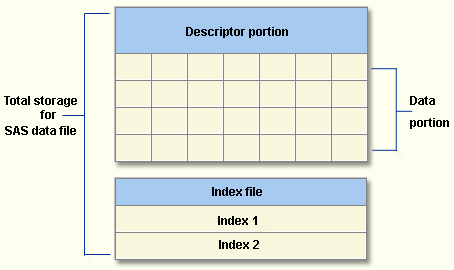
|
In this lesson you learn to use a variety of techniques for minimizing the amount of space that your SAS data files occupy.
|
| This lesson does not cover the Scalable Performance Data Engine (SPD Engine), which is a SAS 9.1 technology for threaded processing. For details about using the SPD Engine to improve performance, see the SAS documentation. |
|
|
1 hour |
|
In this lesson, you learn to
|
|
complete the following lessons:
|